Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex hormonal disorder that affects millions of women all over the world. There are different symptoms of PCOS, however one of the often undiscussed is hair loss. The relationship between PCOS and hair loss requires attention, comprehension, and effective strategies for management.
PCOS, characterized by hormonal imbalances and metabolic irregularities, introduces various challenges for those affected. Among these challenges, the impact of hair health remains significant yet often underestimated. The imbalance of androgens, particularly heightened levels of testosterone, plays a pivotal role in disrupting the natural hair growth cycle.
Understanding PCOS and Its Impact on Hair
According to Johns Hopkins Medicine Health Library, PCOS is a condition where the ovaries overproduce androgen hormones. The hormone androgens are involved in the initiation of hair growth during puberty in underarms and pubic areas.
The hormonal imbalance in PCOS significantly disrupts the normal hair growth cycle. The surplus of androgens causes hair follicles to shrink, resulting in finer hair texture. During severe cases, it might also cause baldness in specific regions. This is a common condition among women with PCOS, termed androgenic alopecia.
Some women may also experience increased shedding or hair loss which leads to reduction in overall hair volume. Hormonal changes can also contribute to scalp conditions like dandruff, oily scalp, or seborrheic dermatitis.
Signs and Symptoms of PCOS-related Hair Loss
PCOS can cause various symptoms which includes hair loss or thinning, known as androgenic alopecia or female pattern hair loss. Here are some signs and symptoms related to PCOS-related hair loss:

Hair Thinning: PCOS-related hair loss often begins with hair thinning at the crown or top of the scalp. This thinning might be gradual and could affect the overall volume and thickness of hair.
Increased Hair Shedding: One of the signs of hair loss related to PCOS is increased hair shedding. Hair falls can increase more than usual when combing, washing, or resting on a pillow. The excess hair shedding occurs due to hormonal imbalances caused by PCOS.
Receding Hairline: Some individuals might experience a receding hairline with polycystic ovary syndrome hair loss, which is similar to male pattern baldness.
Visible Scalp: As hair loss progresses, you may see more of your scalp becoming visible. Thinning hair can make your scalp appear through the remaining strands. This visible scalp is a common sign of hair fall caused by the hormonal changes of PCOS.
Hormonal Changes: PCOS is associated with hormonal imbalances, particularly with elevated levels of androgens (male hormones like testosterone) or an increased sensitivity to these hormones. This hormonal imbalance can trigger hair loss in a similar pattern to male pattern baldness.
Irregular Menstrual Cycles: PCOS often causes irregular periods or might lead to the absence of menstruation.
Acne and Hirsutism: Excessive hair growth in areas where men typically grow hair, such as the face (especially the upper lip and chin), chest, and abdomen, can also be a sign of PCOS. Acne may also be present due to increased androgen levels.
Weight Gain: While weight gain is not directly related to hair loss, weight gain around the abdomen is a common symptom of PCOS.
Causes of Androgenic Alopecia With PCOS
Androgenetic alopecia which is commonly known as male or female pattern hair loss, can be associated with PCOS. Androgenic alopecia is caused due to hormonal imbalances, and here are some of the primary causes:
Androgen Imbalance: PCOS is often involved with higher-than-normal levels of androgens, such as testosterone. This imbalance of hormone can affect the hair growth cycle, leading to miniaturization of hair follicles and eventually causing hair to become thinner and shorter in tis growth phase.
Sensitivity of Hair Follicles to Androgens: Some individuals with PCOS may hair follicles more sensitive to androgens, especially dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a potent form of testosterone. This sensitivity to androgens can lead to the miniaturization of hair follicles, resulting in hair thinning and eventual hair loss.
Insulin Resistance: Insulin resistance is quite common in PCOS. If the insulin levels is high, it can stimulate the production of androgens in the ovaries, contributing to hormonal imbalances that affect hair growth.
Inflammation: Chronic low-grade inflammation is associated with PCOS and can also affect hair follicles, leading to hair thinning or loss.
Genetic Predisposition: Genetics plays a role in androgenic alopecia. Having a family history of pattern baldness can increase the likelihood of experiencing hair loss, especially when coupled with the hormonal imbalances seen in PCOS.
5 PCOS Hair Growth Treatments
The treatment for PCOS hair loss typically involves addressing the underlying hormonal imbalances and managing symptoms. Here are some common approaches used to address polycystic ovary syndrome hair loss in individuals:

1. Medications:
Anti-androgen medications can help block the effects of androgens on hair follicles, reducing hair loss and hirsutism. Oral contraceptives can also regulate hormones and reduce androgen levels, which can help improve hair loss. Medications that manage insulin resistance in PCOS, like Metformin, can also indirectly affect hormone levels.
2. Topical Treatments:
Medications applied directly to the scalp can help treat hair loss caused by PCOS. Over-the-counter topical solutions, such as minoxidil, can stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. It’s applied directly to the scalp.
3. Lifestyle Changes:
Adopting a balanced diet and regular physical activity can help manage insulin levels and reduce hormonal imbalances.
4. Hair Care Practices:
Avoid harsh treatments, tight hairstyles, and excessive heat styling to prevent further damage to fragile hair. Also, use mild shampoos and maintain scalp health that can support better hair growth.
5. Hair Procedures:
Treatments like laser hair therapy or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections might be used to prevent PCOS hair loss and stimulate hair growth.
Learn more on PRP Therapy for Hair Loss.
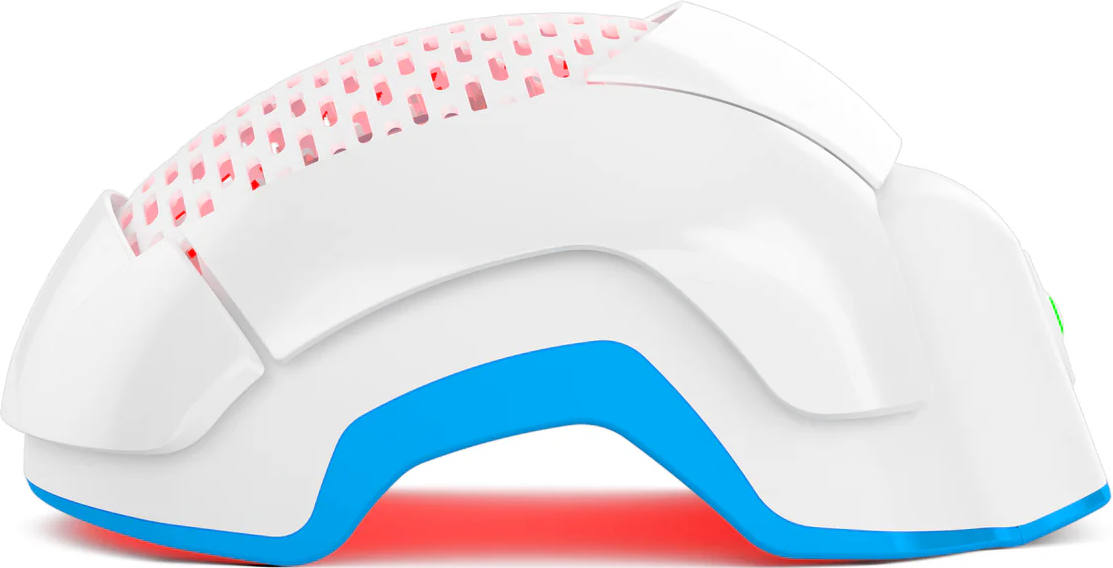
Address PCOS Hair Loss With Laser Hair Therapy
For individuals with PCOS-related hair loss, Theradome might be considered as part of a comprehensive approach to managing hair loss. Theradome helmets can be used as a complementary treatment alongside other PCOS management strategies like medications, lifestyle changes, and hormonal regulation.
Laser therapy’s mechanism involves stimulating hair follicles and potentially improving blood flow to the scalp, which might aid in promoting hair growth. Laser therapy typically requires consistent use over an extended period to see potential results. Patience is crucial, as changes in hair growth often take time.
Experience the power of Theradome's cutting-edge laser therapy for hair regrowth today! Reclaim fuller, healthier hair with our clinically proven device. Start your journey to revitalized hair growth and renewed confidence. Try Theradome now and embrace a brighter, fuller future!
Conclusion
PCOS can lead to hair loss problems for many women. But there are ways to manage this issue. Medications that balance hormones, products applied to the scalp, laser treatments, and healthy lifestyle choices may all help regrow lost hair.
With proper care and the right approach, women with PCOS can control their hair loss and restore thicker, fuller hair. While hair changes from PCOS can be frustrating, don't lose hope; solutions are available to improve symptoms over time. Additionally, you can try the Theradome laser helmet to stimulate hair follicles and promote healthy hair growth.