Let’s tackle a topic that hits close to home for many of us - the receding hairline. Yep, that thing that has us all checking the mirror and wondering where our luscious locks are going. Don’t worry we’ve got your back.
A receding hairline is a common concern affecting both men and women and has a significant impact on self-esteem and overall confidence. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the stages of a receding hairline, its causes, and the diverse treatments available. We’ll delve into the emotional and social aspects of this issue, helping individuals make informed decisions to address it effectively.
What is a Receding Hairline?
A receding hairline is characterized by the hairline gradually moving backward, revealing more of the forehead. It starts with a slight recession at the temples and progresses over time.
Distinguishing between a mature hairline and a receding one is crucial, as a mature hairline is a natural part of aging while a receding hairline indicates potential hair loss.
7 Receding Hairline Stages
A receding hairline normally begins with the hairline gradually moving upward and progresses to more hair loss in the frontal area. A receding hairline is the first sign of male pattern baldness, which progresses in seven stages. Let's look at these stages of a receding hairline:
Stage 1: Minimal Recession
This is the earliest stage of a receding hairline. Your hairline is starting to move back just slightly. There may be a very small amount of hair thinning or the beginning of a tiny bald spot forming, but the changes won’t be noticeable to others. This is a good time to start taking preventative measures.
Stage 2: Early Noticeable Recession
At this point, the hairline has moved back a bit more and the change is becoming easier to see. The recession at the front and temples is starting to create the beginnings of an M-shaped pattern. While still mild, most people will now be able to notice the early progression.
Stage 3: Noticeable Recession
The hairline has now moved back significantly. The M-shape at the temples is more obvious, and the thinning at the front of the head is clearly visible. People around you will likely recognize the hair loss at this stage, and it’s a good time to think about ways to treat your hair loss.
Stage 4: Moderate Recession
At this stage, the hairline has moved back quite a bit. The forehead looks larger and more scalp is visible. The recession forms more of a semicircle shape around the front and sides of the head, and the gaps between hairs are wider, making the scalp easier to see.
Stage 5: Deep Recession
This stage shows a more advanced version of the moderate recession. The M-shape is much deeper, and the frontal hair loss has extended enough that the top of the head appears noticeably sparse. The hairline continues to move upward and backward.
Stage 6: Advanced Recession
The hairline has now receded significantly, with a pronounced M-shape that reaches far back on the scalp. Most of the frontal area shows visible thinning, and the forehead looks very big. The top of the head is close to fully bald.
Stage 7: Severe Recession (Final Stage)
This is the most advanced stage of a receding hairline. The hairline has gone back to the highest point it will reach, and the majority of the top and front of the scalp is bald. Only thin or scattered hair may remain around the sides.
What Causes Receding Hairline?

There are several factors that contribute to a receding hairline, including genetic predisposition and hormonal influences. While receding hairline is more common in men, it can also affect women. Some of the main factors causing receding hairline are:
Genetics (Heredity): The primary cause of a receding hairline is genetics. If your parents or close relatives experienced hair loss or a receding hairline, you are more likely to experience it as well.
Learn More: How Your Genetics Influence Hair Loss
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal changes, particularly the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), play a significant role in hair loss. DHT shrinks hair follicles over time, causing them to produce thinner and shorter hair until they eventually stop producing hair altogether.
Age: Aging is a natural cause of a receding hairline. As you age, the rate of your hair growth slows down, and hair follicles may not regenerate as effectively, leading to thinning hair and a receding hairline.
Poor Diet and Nutrition: A lack of essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and protein, can contribute to receding hairline and hair loss. A well-balanced diet is essential for maintaining healthy hair growth.
Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to hair loss, including a receding hairline. High-stress levels can disrupt the normal hair growth cycle and lead to increased shedding.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions and chronic illnesses can also cause hair loss, including autoimmune diseases, thyroid disorders, and alopecia areata. These conditions can affect the hair growth cycle and lead to a receding hairline.
Smoking and Substance Abuse: Use of certain substances and smoking can negatively impact hair health and contribute to hair loss, including receding hairline progression.
Hairstyling Practices: Excessive use of tight hairstyles (e.g.: ponytails, braids) or harsh hair treatments (e.g.: frequent coloring, perming, straightening) can damage hair follicles and lead to hair loss and a receding hairline progression.
Poor Scalp Health: An unhealthy scalp due to lack of proper hygiene, fungal infections, or excessive oil production can hinder hair growth and contribute to a receding hairline.
How is a Receding Hairline Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of a receding hairline typically involves a medical evaluation by a healthcare professional, usually a dermatologist or a trichologist. Here’s how the diagnosis is typically made:

Medical History and Physical Examination
A detailed medical history, including any family history of hair loss or female/male pattern baldness, is very important to analyze the pattern and progression of your hair loss. A physical examination of the scalp and hair will be conducted to assess the extent and pattern of hair loss.
Scalp Examination
The healthcare professional will closely examine your scalp using specialized equipment and techniques to assess the hair density, quality, and distribution. They may use a magnifying tool or a trichoscope for a closer look.
Hair Pull Test
A pull test may be performed to assess hair shedding. The healthcare professional gently pulls on a small amount of hair to see how many hairs come out.
Scalp Biopsy
In some cases, a scalp biopsy may be performed to examine a small piece of scalp tissue under a microscope. This helps to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes of hair loss.
Blood Tests
Blood tests can also be conducted to check for underlying medical conditions that could be contributing to hair loss, such as hormonal imbalances, thyroid disorders, iron deficiency, or health issues.
Photographic Documentation
Before and after photos may be taken to track the progression of hair loss and the effectiveness of any treatments over time.
How to Stop Receding Hairline?
While complete reversal of a receding hairline may not be possible, there are several treatments and strategies that can help slow down the progression and improve the appearance of the hairline. Here are some treatment methods for stopping receding hairline:
Medications
Minoxidil (Rogaine) is an OTC topical medication that can help slow down hair loss and stimulate hair growth. Finasteride (Propecia) is a medication for men only and works by blocking the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is associated with hair loss. The reason finasteride should not be used by women is due to the risk of birth defects.
Hair Transplantation
Hair transplantation is a surgical technique that effectively treats receding hairline. There are surgical procedures that involve taking hair follicles from a donor area (usually the back or sides of the head) and transplanting them to the areas with receding or thinning hair.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
In PRP Therapy, a patient’s blood is drawn, processed to concentrate the platelets, and then injected into the scalp. Injecting the PRP is believed to promote hair growth, thicken existing hair, and stop receding hairline.
Microneedling
Microneedling involves using a device with tiny needles to create micro-injuries in the scalp, which can stimulate hair growth and increase the absorption of topical treatments.
Hair Loss Shampoos and Conditioners
Some specifically formulated shampoos and conditioners reduce hair loss and promote a healthier scalp. Ingredients like ketoconazole or saw palmetto are used in such shampoos and conditioners.
Diet and Lifestyle Changes
A healthy diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins can support overall hair health. Consider incorporating foods like leafy greens, nuts, seeds, eggs, and fish into your diet.
Also manage stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and other stress-reducing activities, as stress can contribute to hair loss.
If you want a quick and easy hack to disguise your receding hairline, you can go through our article about seven easy tips and tricks to cover up your receding hairline, and don't let it shake your confidence.
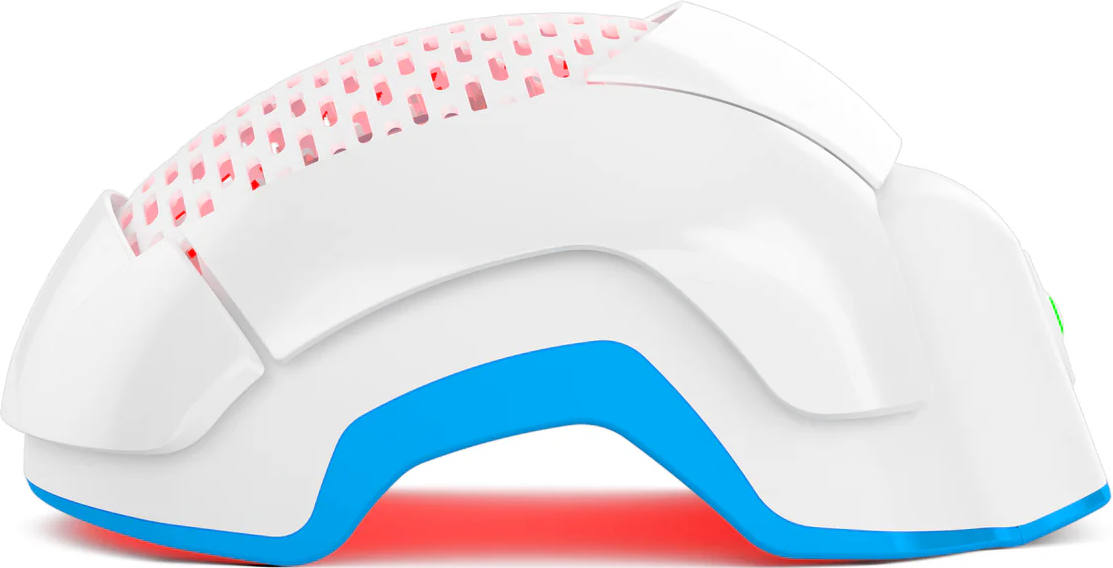
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
LLLT involves using red light therapy to stimulate hair growth. Devices like Theradome hair growth helmets can be used at home to expose the scalp to low-level laser light.
In addressing a receding hairline, Theradome offers a promising approach through its wearable laser therapy helmet, utilizing low-level laser light to potentially stimulate hair follicles and encourage hair growth. Incorporating Theradome into your hair care routine may contribute to improved hair density and quality over time.
If you’re interested in exploring Theradome as a potential solution for your receding hairline, consider using it along with other hair loss treatments. Stay informed about the latest advancements and learn how Theradome can be integrated into your personalized hair care regimen for the best possible outcomes.