Hair loss is a multifaceted condition affected by various factors, and genetic predisposition plays a big role in it. Our genes, the things we inherit from our parents, play a big part in deciding if we’ll lose hair and when it might happen.
Our genes have a say in how our hair grows and stays on our heads. Sometimes, certain genes can make our hair thinner or fall out, causing what we know as baldness. This is especially true for things like male or female pattern baldness. Other times, our immune system can attack our hair, leading to patches of hair loss—this is called alopecia areata.
If you notice any family members losing hair, it might mean you could too. But it’s not always straightforward. Hair loss doesn’t always pass down from just one parent. Genetic hair loss can come from both sides of the family, making it a bit tricky to predict.
Types of Hair Loss
Hair loss can occur due to various reasons, and there are different types of hair loss conditions. Here are some common types:

Androgenetic Alopecia (Male/Female Pattern Baldness): This is the most common type of hair loss which is characterized by a gradual reduction in hair volume, typically along the temples and crown in men and diffuse thinning in women. The chances of developing androgenetic alopecia is largely determined by genetics, with several genes involved in the development of the condition.
Alopecia Areata: Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks hair follicles, causing sudden hair loss in patches on the scalp or other body parts.
Telogen Effluvium: This type of hair loss occurs due to significant stress, trauma, hormonal changes, or certain medications, leading to a larger than usual amount of hair shedding during the telogen (resting) phase of the hair growth cycle.
Traction Alopecia: It results from constant pulling or tension on the hair, often due to hairstyles like tight ponytails, braids, or extensions, leading to hair breakage and loss.
Anagen Effluvium: Usually caused by chemotherapy or radiation treatment, this type of hair loss affects the anagen (growth) phase of the hair cycle, resulting in sudden and severe hair shedding.
Hair Structure Genes: The structure of your hair is also influenced by genetics along with hair texture, thickness, and growth rate. They are all determined by the hair production genes. The hair will be more susceptible to damage, breakage, and loss if there are differences in these genes.
Where Do Your Hair Genes Come From?
Hair genes, like all our genes, come from our parents. We inherit them from both our mother and father, including the genes that determine our hair color, texture, density, and other hair-related traits. These genes are located on chromosomes and are passed down through generations. Variations in these genes result in a diverse range of hair types and characteristics along with hair loss conditions.
Read More: Thick or Thin Hair: How to Identify Your Hair Type
Yes, hair loss can be hereditary. It is estimated that 80% of cases of androgenetic alopecia are due to genetic factors. However, genetics is just one of the several factors that influence hair loss. There are several other factors that can influence hair loss.
5 Signs of Genetic Hair Loss
There are various signs you can look out to identify genetic hair loss. Here are some common signs and symptoms you need to look out for:
1. Gradual Thinning on Top of Head
One common sign of hereditary hair loss is gradual hair thinning on the top of the head. You may notice your hair becoming lighter and less full, especially at the crown or front of your scalp. Hair thinning happens slowly, so it can be easy to miss at first, but the thinning will continue if the underlying genetic condition is not addressed.
2. Circular or Patchy Bald Spot
Some people with genetic hair loss get smooth, round, or patchy bald spots instead of overall thinning. In these cases, hair falls out in one area, leaving a small, distinct bald circle or oddly shaped patch of bare scalp. The skin looks normal but is completely missing hair follicles. These bald spots can appear on the head's top, sides, or back.
3. Sudden Hair Loss
For some people, hair loss from genes can happen quite suddenly rather than gradually over time. They may notice an alarming amount of hair coming out when washing, brushing, or just running their fingers through it.
4. Full-Body Hair Thinning
While hair loss on the scalp is most common, some people with genetic hair loss see thinning happen all over their body, too. In addition to losing hair on the head, they may notice their eyebrows, eyelashes, arm hair, leg hair, and other body hair getting sparser over time. The hair everywhere gradually gets finer and thinner until it nearly disappears in some areas.
5. Receding Hairline
Another common sign is a receding hairline. Gradually, you may notice your forehead getting larger as the hair at your temples and the front of your scalp starts to thin and pull back. This gradual hairline recession is a classic symptom of the inherited condition known as pattern baldness or androgenetic alopecia.
Male vs Female Pattern Baldness
Male pattern baldness and female pattern baldness differ in their typical patterns and causes.
Male pattern baldness typically starts with a receding hairline and thinning at the crown. Over time, hair loss progresses, leading to a horseshoe-shaped pattern of hair around the sides and back of the head. Male pattern baldness is primarily influenced by genetics and hormones (specifically DHT or dihydrotestosterone, a derivative of testosterone). Hair follicles sensitive to DHT shrink, leading to shorter and finer hair until they stop growing altogether.
Find out more on DHT induced hair loss.
Meanwhile, in female pattern hair loss, women tend to experience a more diffuse thinning across the scalp rather than a distinct receding hairline. The hair becomes thinner all over the head, and in some cases, hairline recession can occur. Genetics and hormonal changes play a role, particularly fluctuations in androgens that can occur due to factors such as ageing, hormonal imbalances, or certain medical conditions.
While both types share similarities in terms of genetic predisposition, the progression and specific patterns of hair loss can differ between males and females. Also, other factors like stress, certain medical conditions, medications, and lifestyle habits can contribute to hair loss in both men and women.
How To Prevent Genetic Hair Loss?
While there are some cases of hair loss that can’t be prevented, there are some measures you can take to reduce the risk of hair loss. Here are some of them:

Healthy Diet: Ensure that you’re consuming adequate nutrients, especially vitamins and minerals like iron, zinc, and vitamins A, C, D, and E, as deficiencies can contribute to hair loss. Staying hydrated by drinking water also helps hair follicles function better. A balanced, nutritious diet gives hair the building blocks it needs to prevent genetic hair loss.
Gentle Hair Care: Being gentle with your hair helps keep it strong against genetic hair loss. Avoid excessive styling, harsh chemicals, and heat. Be gentle when brushing or styling to prevent breakage.
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to hair loss. Techniques like meditation, yoga, or exercise can help reduce stress levels.
Avoid Tight Hairstyles: Constantly pulling your hair tight in styles like ponytails or braids can cause traction alopecia, leading to hair loss.
Limit Use of Hair Products: Avoid or limit the use of products that contain harsh chemicals that can damage the hair. Opt for natural or mild products.
Regular Scalp Message: Massaging your scalp can stimulate blood flow to the hair follicles, promoting hair growth.
Medical Conditions: Consult with a healthcare professional to address any underlying medical conditions contributing to hair loss.
Avoid Smoking: Smoking can contribute to hair loss, so quitting or reducing smoking can be beneficial.
Use Gentle Shampoos: Choose shampoos that are gentle on your scalp and hair, avoiding those with harsh chemicals that may damage the hair follicles.
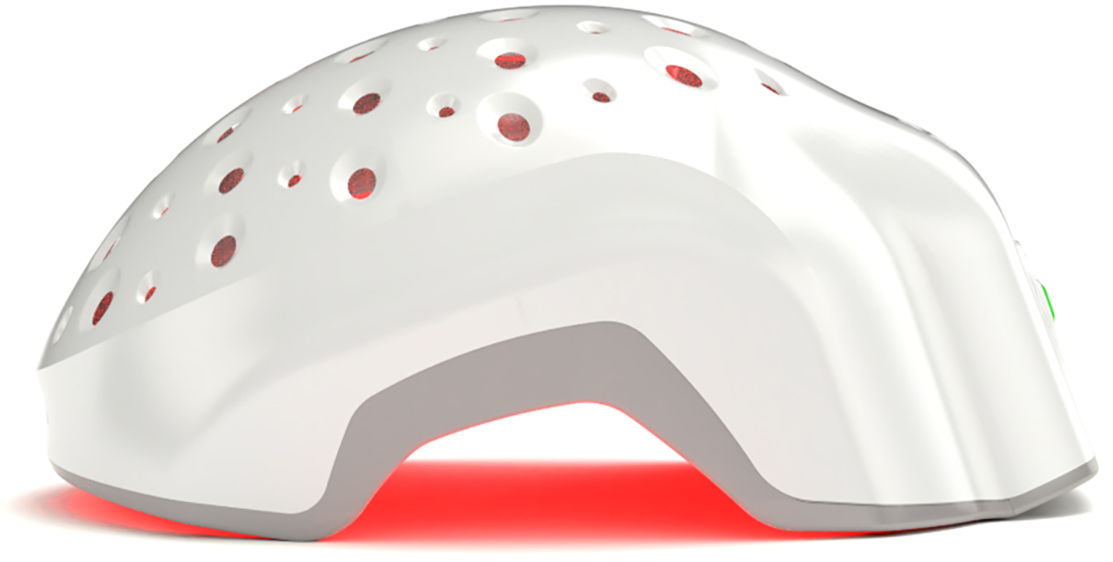
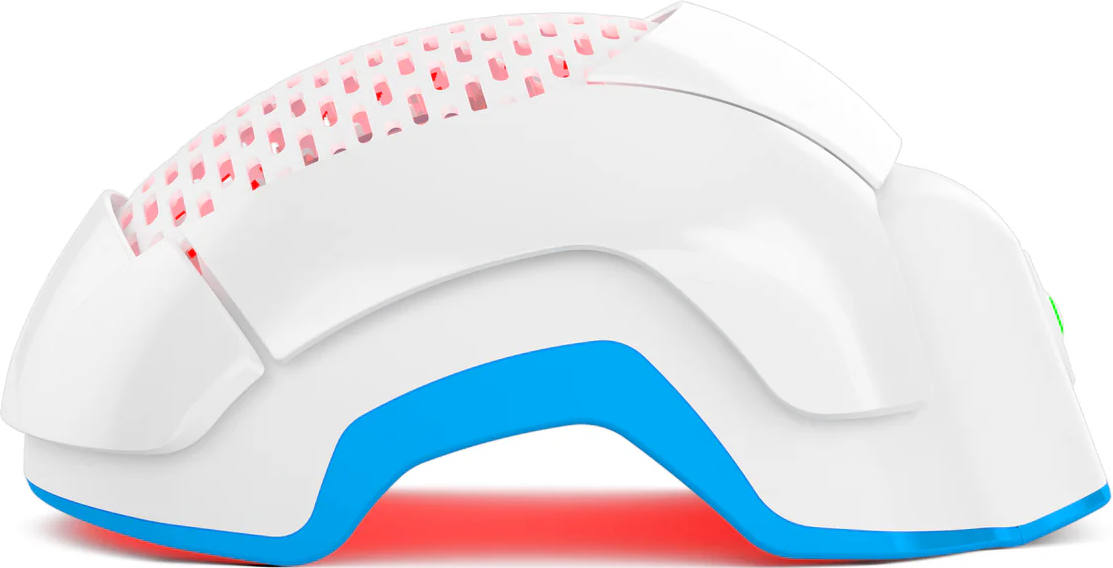
Theradome - Prevent Hair Loss Starting Today!
Theradome is a laser hair growth helmet designed to slow down hair loss and stimulate hair regrowth. The concept behind Theradome is based on low-level laser therapy (LLLT), which is believed to stimulate hair follicles, increase blood flow to the scalp, and promote hair growth.
Users can typically wear the Theradome helmet for specified periods (usually a few minutes per session, several times per week) to potentially see results over time. Theradome is best for individuals experiencing certain types of hair loss, like androgenetic alopecia, if used consistently.
Experience the power of rejuvenation with Theradome - Transform your hair health today! Try Theradome's cutting-edge laser therapy helmet to stimulate hair growth and potentially combat hair loss. Take the first step towards fuller, healthier hair. Discover the Theradome difference now!