You all have heard about diabetes, right? It is a disease affecting millions of people worldwide. Diabetes is a chronic health condition that occurs when the body is unable to properly regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels. But do you know that diabetes also contributes to hair loss?
Yes, diabetes can lead to hair loss and thinning hair for some people. Hair loss is a potential complication of diabetes caused by poor blood sugar control. When diabetes raises blood glucose levels too high, it can disrupt the normal hair growth cycle and lead to excessive shedding. While diabetes doesn't directly cause hair loss in the same way, it causes symptoms like increased thirst or frequent urination. It still plays a role that leads to hair loss.
Yes, genes are often a factor, but suddenly losing large quantities of hair could indicate that something's not quite right. Sometimes, an underlying medical condition, including diabetes, is to blame. Let’s take a look at the relationship between diabetes and hair loss – and how laser hair therapy can help if you’re one of the millions of individuals diagnosed with diabetes every year.
How Diabetes Affects the Body and Hair Growth Cycle?
People with diabetes have difficulty in making enough insulin, using insulin effectively, or both. Insulin is a helper hormone that moves sugar from the food you eat in your bloodstream into your body's cells. These cells can then use the sugar for energy or store it.
If there's not enough insulin or it doesn't work well, then sugar can build up in your bloodstream. These high blood sugar levels can cause harm to other parts of your body, like kidneys and eyes. It can also damage nerves and blood vessels.
Blood vessels are responsible for carrying oxygen all around your body to keep your organs and tissues healthy. If these blood vessels are damaged, then they might fail to deliver enough oxygen and nutrients to help your hair follicles, which are roots of your hair. As a result, your hair's usual growth cycle can be disturbed, and you might notice changes in your hair.
Here, let's dive deep into how diabetes causes hair loss:
1) Diabetes affects blood flow.
Diabetes affects blood circulation, and not in a good way. Extremities like your feet and hands are not the only things affected: blood flow is compromised in the scalp area as well.
So what happens next? Blood carries nutrients. Hair cells need nutrients to divide and replicate, and eventually, these cells form hair follicle tissue. If you’re healthy, hair follicle tissue thickens into cuticles, which grow into healthy, terminal hair. But if you’ve been diagnosed with diabetes, hair follicles thin out, and eventually, hair follicles are miniaturized. Your existing hair weakens and sheds, while a lack of nutrients on the scalp prevents new hair growth. Discover actionable tips and techniques on how to stop hair shedding.
While some diabetics can regrow their hair without any assistance, numerous individuals often need help; and since laser hair therapy is a natural solution to diabetes hair loss with no side effects, it’s always the best way to go.
2) Diabetes causes easy bruising.
When small blood vessels rupture and leak blood under the skin, a pool of blood accumulates, causing visible bruises. In some individuals, the bruises formed from diabetes can lead to hair loss. Bruises are generally a color discoloration that occurs when tissues below the skin surface are injured.
There are many causes of bruises. Some people with medical conditions like diabetes are also prone to bruises, but it's not true that people with bruises always have diabetes. The high sugar level in diabetic people damages the blood vessels over time. Damaged blood vessels cannot circulate proper oxygen and nutrients to all the cells, causing cells responsible for wound healing not to function properly. This causes the formation of small round, reddish, or brownish-like patches called bruises. Minor bruises generally go away on their own within a few days, but it is a must to see a medical practitioner if it is critical.
3) Diabetes weakens the immune system.
Any type of disease or illness weakens the immune system. In this case, your body needs to work much harder to fight off any type of infection – including infections attacking your scalp. Anyone with an enfeebled immune system will be more prone to fungal disease, including ringworm, which can result in patchy hair loss and overall hair thinning.
On top of this, the healing process for diabetic hair loss takes much more time than for healthy individuals. This means that anagen hair (which belongs to the growth phase) becomes energy-deprived and can never really blossom. In other words, your scalp suffers from a compromised hair growth cycle, which might lead you to lose hair.
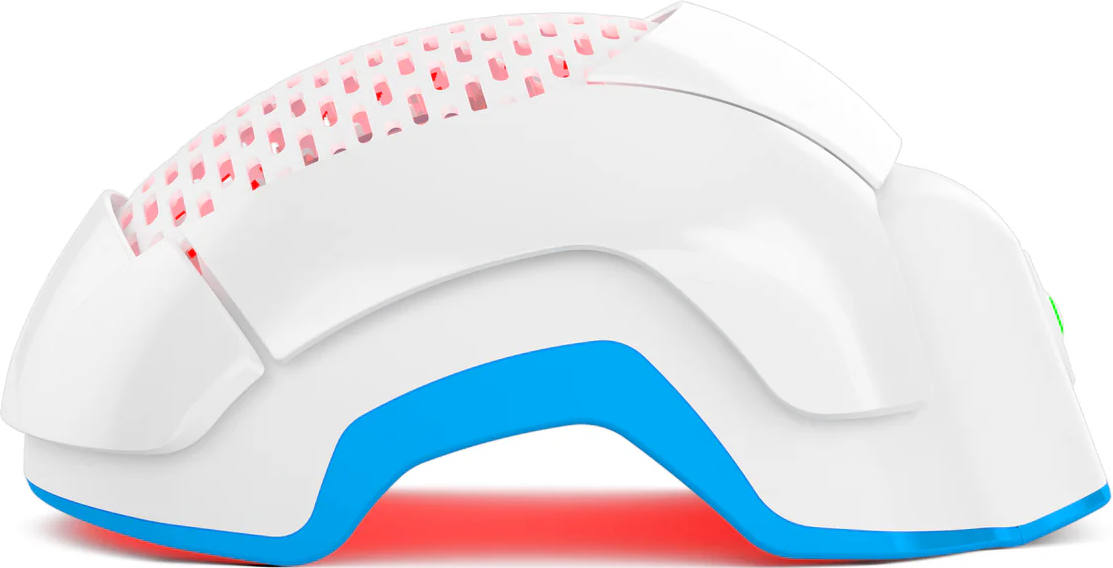
Keep in mind that regardless of your health, you can strengthen your hair follicles with the Theradome. And don’t forget that laser hair growth therapy is clinically proven to shift hair in the anagen phase, which prevents hair loss.
4) Diabetes induces hormonal changes.
Diabetes can trigger changes in your body's hormone levels, which play a key role in hair growth and health. Ever heard of the term telogen effluvium? It specifically includes hair loss due to drastic hormonal changes. Hormonal changes can push hair follicles into a "resting phase," leading to more shedding and thinner hair over time. Additionally, diabetes-related stress and inflammation can worsen these imbalances, which can lead to diabetic hair loss.
6 Signs of Diabetes Hair Loss
The signs of diabetes hair loss can be difficult to identify since there are hundreds of possible reasons for hair loss. However, the following signs and symptoms might help you recognize if excessive shedding is being caused by diabetes:
1. Excessive hair falling out:
When diabetes causes problems with blood sugar levels, it can affect your whole body, even your hair. You might notice more hair strands than usual falling out when you brush, wash, or run your fingers through your hair. It isn't just losing a few strands; you may find large clumps of hair on your pillow, in the shower drain, or on your clothes. The sudden increase in hair loss can be alarming and is often one of the first signs of diabetic hair loss.
2. Overall hair thinning:
If your hair feels thinner all over the scalp, it could be linked to diabetes. High blood sugar can weaken hair growth and make hair look less full. It’s a subtle change but worth paying attention to.
3. Patchy bald spots:
Noticing small bald spots on your scalp can be a sign of diabetes hair loss. It happens when blood flow to the hair follicles is reduced, causing hair to fall out in patches. If you see these bald spots, talking to your doctor is a good idea.
4. Full body hair loss:
People with diabetes may experience hair loss not just on their heads but all over their bodies. Hair fall can occur from the arms, legs, chest, and even eyebrows. The widespread hair loss happens because diabetes affects hormone levels and blood flow throughout the entire body, not just in one area. When blood sugar levels remain high, it can impact hair follicles everywhere, leading to noticeable thinning or loss of body hair in multiple areas.
5. Dry, brittle texture:
People with diabetes often notice their hair becoming dry, rough, and brittle, making it more likely to break and split. If your hair feels rough or looks dull instead of shiny, it may be a sign that diabetes is affecting the hair.
6. Slow regrowth:
Slow regrowth is a sign of hair loss that can happen with diabetes. If you notice that your hair takes a long time to grow back after it falls out, this could be linked to the condition. Diabetes can disrupt the normal hair growth cycle, making it harder for hair to regrow quickly. Even after getting blood sugar under control, any new hair growth comes in slowly and looks thin at first.
Can Diabetic Medications Cause Hair Loss?
Yes, some diabetic medications like Metformin, SGLT2 inhibitors, and Mounjaro may contribute to hair loss, though this side effect is not common for all drugs. For example, long-term use of metformin, a widely prescribed medication for type 2 diabetes, can reduce vitamin B12 absorption in the body. Low B12 levels are linked to hair thinning or shedding. Other medications, like certain blood pressure or cholesterol-lowering drugs prescribed alongside diabetes treatments, may also list hair loss as a possible side effect.
If you notice hair thinning while taking diabetes medications, talk to your doctor. They may check for nutrient deficiencies (like B12) and recommend supplements or adjust your treatment plan. In many cases, managing blood sugar levels effectively can help reverse diabetic hair loss over time.
Will Hair Loss from Diabetes Grow Back?
Yes, diabetes-related hair loss can usually grow back. Maintaining proper blood sugar levels can reduce hair shedding and promote faster hair regrowth in previously affected areas. However, this is not the same in all cases. Some may experience better improvements faster, while others may require more time for significant results. The outcome depends on various factors like diabetic medications, dietary system, and lifestyle that you are having.
How Do Different Types of Diabetes Cause Hair Fall?
Hair loss is a common symptom of diabetes, affecting both type 1 and type 2 diabetes patients. The main causes are believed to be hormonal imbalance, restricted blood flow due to high blood sugar levels, and in some cases, an autoimmune reaction. Maintaining blood sugar levels through diabetic medication, diet, and exercise can help prevent and even reverse diabetes-related hair loss.
We have discussed major types of diabetes and their role in hair loss:
Type 1 Diabetes Hair Loss:
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the pancreas, causing insulin-producing cells to get damaged. The main purpose of insulin is to use glucose for energy by moving it from the bloodstream into cells. When this process is disrupted, the blood sugar level increases, which damages the blood vessels of different body types, including those in the hair follicles. As a result, conditions like Alopecia areata and hair loss may occur side by side. The loss occurs in the form of small and round patches,
Type 2 Diabetes Hair Loss:
People with type 2 diabetes are often prone to hair loss. It is categorized as insulin resistant, where the body's cells can't effectively respond to the insulin. This causes an increase in sugar levels in the bloodstream, which causes blood vessel damage in the hair follicles, leading to type 2 diabetes hair loss. Insulin resistance can also lead to an imbalance in the hormone, causing an increase in androgens. Overstimulated androgens also cause hair follicles to shrink and produce thinner hair, leading to androgenetic alopecia which directly affects the lifecycle of the hair growth cycle.
Gestational Diabetes:
Diabetes diagnosed for the first time during pregnancy is what we call as Gestational diabetes. According to research conducted by the CDC on Prevalence Estimates of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus, 1 in 20 (4.6%) pregnancies in the United States are affected with Gestational diabetes, and about half of women who develop gestational diabetes will be more prone to develop type 2 diabetes after pregnancy. The Placental Hormone, which produces many hormones during pregnancy, naturally increases insulin resistance. Elevated insulin increases the glucose level in the bloodstream. The blood vessels, including those in hair follicles, are then damaged, leading to hair loss and hair thinning. This way, gestational diabetes causes hair loss, and many people associate hair loss with pregnancy.
Treatment and Management of Diabetes for Hair Loss
Diabetes induced hair loss treatment and management involve a combination of strategies that aims at controlling high blood sugar levels, promoting overall health, and stimulate hair growth. Here are some steps to consider on how to stop hair loss from diabetes effectively:
1. Manage blood sugar levels:
Timely management of sugar levels is necessary. You must follow proper recommendations for insulin or medication and monitor blood sugar regularly to maintain optimal levels.
2. Adopt a Balanced Diet:
Adopt a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Limit your intake of refined sugars and carbohydrates and reduce serving sizes.
3. Engage in Regular Physical Activity:
Regular exercise can lower blood sugar levels by making the body more sensitive to insulin, which helps cells absorb sugar for energy.
4. Manage Stress:
Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or mindfulness to alleviate stress, which can impact hair health.
5. Maintain Scalp Health:
Keep your scalp clean and well-moisturized. Use mild, sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners.
6. Consume Nutrient-Rich Foods:
Consume food rich in nutrients that promote hair health, such as zinc, biotin, vitamins A and C, and omega-3 fatty acids.
There are also certain medications that can help treat diabetes related hair loss and help hair regrow. If alopecia areata is causing hair loss, steroid medications can be used to reduce inflammation. Topical drugs such as minoxidil (Rogaine) are also prescribed by dermatologists or skin care specialists.
Protect your health (and your hair!)
If you think that you might have diabetes, and are experiencing symptoms such as hair loss, bruises, and wounds due to poor circulation, book an appointment with your physician immediately. Diabetes, if left untreated, can cause severe, irreparable damage to your body – and we’re not just talking about your hair. If not addressed properly, diabetes can cause nerve damage as well as damage to your heart, eyes, kidneys, and blood vessels.
First, consult your doctor and decide on a treatment course; for instance, did you know that Type 2 diabetes could be treated with simple lifestyle changes? Once you’ve addressed the root of the problem, you can focus on re-growing your hair in the comfort of your home with the FDA-cleared Theradome LH80 PRO. The Theradome helmet is suitable for all hair types.
Your path to luscious, fuller hair begins with Theradome's laser helmet. Act decisively and grab the opportunity for hair rejuvenation. Don't wait – seize the chance for a better tomorrow!
Other Treatments for Diabetic Hair Loss
Several treatment options can help manage alopecia related to diabetes. Minoxidil, an over-the-counter medication applied directly to the scalp, can stimulate hair growth. Doctors may recommend prescription medications like finasteride for some patients, particularly men experiencing pattern baldness alongside diabetes. Natural approaches such as scalp massage can help improve blood circulation to hair follicles, while biotin supplements may support healthy hair growth when taken as directed by a healthcare provider. Some patients find success with platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, where platelets from their blood are injected into the scalp to promote hair growth.
Conclusion
Diabetes can indeed cause hair loss due to various factors like poor blood flow, hormonal changes, and a weakened immune system. While there are various treatments available, managing blood sugar levels and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are crucial steps. For those seeking a safe and effective solution, the Theradome Helmet stands out as the best option for treating diabetic hair loss, offering a non-invasive way to promote hair growth with no side effects.