Hair is considered a crowning glory, symbolizing a person’s youth, vitality, and confidence. However, as we age, changes in our hairline can occur, causing concern for many individuals. Two common terms used to describe alterations in the hairline are “mature hairline” and “receding hairline.”
Understanding the difference between a mature hairline and a receding hairline is important for anyone noticing changes in their hair. A mature hairline is a natural part of aging, where the hairline moves slightly higher on the forehead. This process is gradual and doesn't usually lead to significant hair loss.
On the other hand, a receding hairline can be a sign of hair loss that may continue over time. It often starts with thinning at the temples and can progress, leading to bald spots. But how can you tell the difference between a mature vs receding hairline? Let’s delve deeper into these concepts to discover the characteristics, differences, and potential treatments
What is a Mature Hairline?
A mature hairline refers to a natural developmental stage where the hairline shifts slightly higher or recedes marginally. It's a benign and normal occurrence typically observed in early adulthood, often during the late teens to early twenties. It's slightly higher and more defined than a juvenile hairline, the lower, rounder hairline you have as a child. The change from juvenile to mature is a normal part of growing up for most men. Unlike a receding hairline associated with male pattern baldness, a mature hairline doesn’t signify imminent hair loss or balding. Instead, it denotes the stabilization of the hairline after the adolescent hairline phase.
What Does a Mature Hairline Look Like?

A mature hairline typically refers to the natural progression of the hairline as a person ages, especially in men. A slight recession at the temples often characterizes it without significant thinning or loss of hair in other areas.
Unlike male pattern baldness, which typically starts with a receding hairline and thinning on the crown, a mature hairline isn’t associated with extensive hair loss. Instead, it’s a natural change where the hairline might move slightly higher or recede a bit at the temples, creating a more “M” or “V” shape.
Diagnosing Mature Hairlines
Diagnosing a mature hairline involves understanding the natural progression of hair loss and changes in the hairline as a person ages. Here are some general guidelines to consider when assessing a mature hairline:
Location of Hairline: A mature hairline typically involves a slight recession at the temples. This might create a more “M” or “V” shape at the front of the hairline. It’s important to note that a mature hairline varies among individuals, and not everyone will have the same pattern.
Stability of Hair Loss: With a mature hairline, the recession at the temples tends to stabilize without significant thinning or loss of hair in other areas of the scalp. Hair loss is usually limited to the front temporal regions rather than affecting the top or crown of the head.
Age Consideration: A mature hairline often starts to manifest in late adolescence or early adulthood, usually in a person’s 20s or 30s. It’s considered a normal part of aging and isn’t typically associated with rapid or extensive hair loss.
Gradual Progression: Hairline changes associated with a mature hairline occur gradually over time. It’s a slow process and doesn’t lead to rapid hair loss or balding patterns, characteristic of conditions like male pattern hair loss.
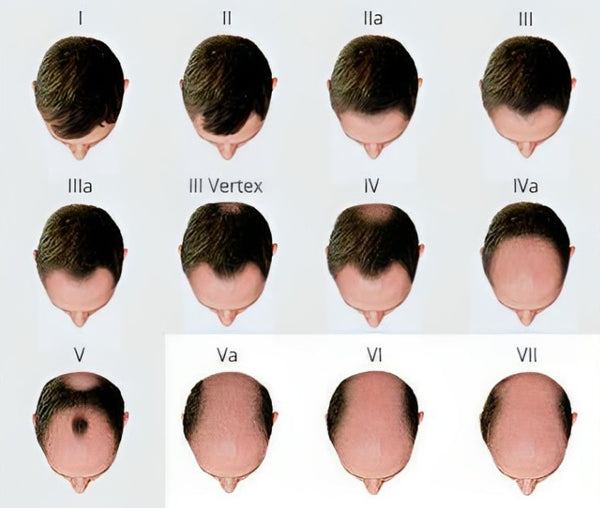
What Stage Are You at on the Norwood Scale?
The Norwood Scale aids in categorizing the severity and progression of male pattern baldness. Stages range from minimal hairline changes (Stage 1) to advanced baldness (Stage 7), helping individuals and professionals gauge the extent of hair loss.
Is a Mature Hairline a Sign of Male Pattern Baldness?
A mature hairline is not necessarily a sign of male pattern baldness. It’s a natural and normal change that occurs as men age, usually in their late teens, twenties, or early thirties.
It is considered part of the natural aging process rather than a precursor to male pattern baldness since all men produce testosterone and DHT. On the other hand, male pattern baldness is a hereditary condition characterized by a predictable pattern of hair loss, usually starting with a receding hairline or hair thinning or both at the crown of the head.
What is a Receding Hairline?
A receding hairline is a condition where the hairline gradually moves backward, typically leaving more of the forehead exposed. It’s a common issue that often occurs as people age, particularly in men. It’s characterized by thinning or loss of hair at the temples and/or the crown of the head, leading to the “receding” appearance. This process is often driven by genetics but can also be influenced by factors like hormonal changes, certain medical conditions, or lifestyle choices.
Also Learn: 5 Signs to Identify Receding Hairline
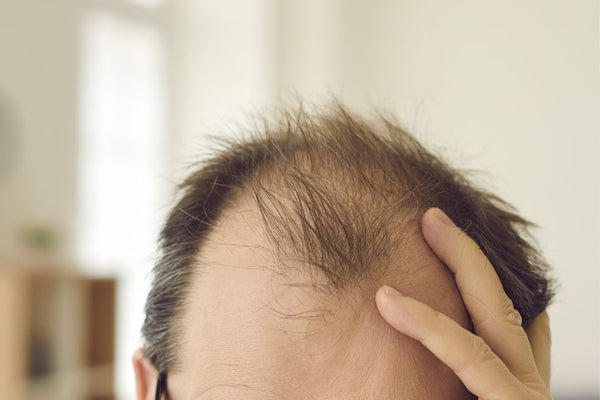

Maturing Hairline vs Receding Hairline: What's the Difference?
A maturing hairline and a receding hairline can sometimes appear similar, but they signify different things.
A maturing hairline is a natural part of aging for many individuals, especially men. It involves a slight recession of the hairline as you get older, typically starting in the late teens to early twenties. With a maturing hairline, the entire hairline recedes slightly, usually creating a V-shaped or M-shaped pattern, but it stabilizes after a while and doesn’t progress dramatically.
On the other hand, a receding hairline refers to a more significant and noticeable loss of hair along the hairline. It’s often an early sign of male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia) and can begin at different ages, sometimes as early as the late teens or early twenties. Receding hairlines tend to recede further, creating a deeper M-shaped hairline or a more extensive recession that can lead to baldness in severe cases.
The main difference between a mature vs receding hairline lies in the extent and progression of the hair loss. A maturing hairline usually stabilizes over time without significant hair loss, while a receding hairline progresses, resulting in more noticeable hair loss and potentially balding in the affected areas.
How to Differentiate a Mature or Receding Hairline?
Distinguishing between a maturing hairline and a receding hairline can be a bit challenging, especially in the initial stages. However, a few key differences can help you differentiate between mature and receding hairline.
Location of the Hairline
A maturing hairline typically involves a slight, symmetrical recession at the temples. It might form a shallow M-shape or a gentle V-shape without significant hair loss elsewhere.
A receding hairline, on the other hand, involves a more noticeable and asymmetrical recession. It often begins at the temples but progresses further, creating a deeper M-shaped hairline, and may extend to the crown or other areas on the scalp.
Progression Over Time
A maturing hairline tends to stabilize after a certain point. Once it has receded slightly, it usually doesn’t progress significantly and doesn’t lead to extensive hair loss.
A receding hairline, however, continues to recede gradually over time. It’s often accompanied by thinning and loss of hair in the frontal and temporal areas, sometimes leading to baldness if left untreated.
Rate of Hair Loss
You can identify a mature or receding hairline by observing the rate of hair loss. With a maturing hairline, the hair loss is gradual and generally doesn't result in large amounts of hair falling out. It's more about the slight shift in the hairline's position.
Receding hairline involves a more noticeable and continuous loss of hair. Hair may shed in larger quantities, especially during showering or grooming.
Family History and Age
If your close relatives, like your father or uncles, have experienced significant hair loss, there’s a higher likelihood that your hairline might be receding rather than just maturing.
The age at which you’re experiencing changes in your hairline can also be a factor. A maturing hairline typically begins in the late teens to early twenties, while a receding hairline might start around the same time or even earlier.
Learn more on how your genetics influence hair loss.
Side-by-Side Comparison of Mature vs Receding Hairline: 5 Major Differences
Here's a simple breakdown of the five big differences between a mature and a receding hairline. This comparison will help you figure out what's happening with your hair.
| Characteristic | Mature Hairline | Receding Hairline |
|
1. Cause |
Mature Hairline occurs naturally with age. |
Receding Hairline is caused by Male Pattern Baldness(Androgenetic Alopecia). |
| 2. Recession | Mature hairline remains relatively stable. | Whereas, a receding hairline recedes, exposing more of the forehead. |
| 3. Hairline Shape | Defined, even shape. | M-shaped or uneven hairline. |
| 4. Hair loss | No further hair loss expected. | Can lead to thinning hair and baldness on the crown. |
| 5. Onset | A mature hairline usually starts in the late 20s or late teens. | A receding hairline can start at any age after puberty. |
Also Read: How to differentiate between a big forehead and a receding hairline?
What’s the Difference Between a Man’s and a Woman’s Receding Hairline?
Both men and women can experience a receding hairline, but there are some differences in how it typically manifests between the genders.
Male pattern baldness, or androgenetic alopecia, is the most common cause of receding hairline in men. It often starts with hair thinning at the temples, creating a characteristic M-shaped pattern. The hair loss tends to progress gradually from the frontal hairline and temples, moving backward over time, eventually leading to baldness in the affected areas. Hormonal factors, especially DHT, play a significant role in male pattern hair loss.
Meanwhile, in women, the hair loss pattern differs from that of men. Instead of an M-shaped pattern, the female hairline recession may involve a more diffuse thinning of hair along the part line or across the entire scalp. Hormonal changes that are related to pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, or conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can contribute to hairline recession in women. Also, genetics, stress, and certain medical conditions can play a role. Female hair loss patterns might not follow specific M-shaped recession; instead, they can present as overall thinning, widening of the part, or a diffuse reduction in hair density along the frontal hairline.
Treatment for Maturing and Receding Hairline
Since a mature and receding hairline are so different from each other, their treatment methods are also dissimilar. Treatment for a maturing or receding hairline can vary based on the cause, severity, and individual factors. Let's explore the treatment methods for each of the hairlines.
Treatment for maturing Hairline
A maturing hairline, a natural part of aging for many individuals, might not necessarily require treatment as it doesn’t typically result in significant hair loss. Here are some approaches you can consider if you’re concerned with the appearance of your hairline:

Hair Products: Using hair products like volumizing shampoos, conditioners, and styling mousses can add thickness and volume to your hair, making it appear fuller.
Cosmetic Hairstyles: Styling your hair in a way that compliments a maturing hairline can make it less noticeable. Longer hairstyles, textured cuts, or hairstyles that sweep the hair forward can help camouflage the receding areas.
Healthy Lifestyle: Ensuring you have a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, managing stress, and avoiding harsh hair treatments can support overall hair health.
Minoxidil (Rogaine): Although Minoxidil is primarily used for treating male pattern baldness, some individuals use minoxidil to maintain hair density and possibly slow down further recession in a maturing hairline.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Devices emitting low-level laser light to the scalp can potentially stimulate hair follicles and promote healthier hair growth. While primarily used for addressing hair loss, it might also aid in maintaining existing hair.
Treatment for Receding Hairline
Treating a receding hairline often involves various approaches aimed at slowing down hair loss, promoting regrowth, or managing the appearance of the receding hairline. Here are some common treatments:

Minoxidil (Rogaine): Available over-the-counter, minoxidil is a topical solution applied directly to the scalp. It can slow down hair loss and, in some cases, stimulate new hair growth. It’s approved for use in both men and women.
Finasteride (Propecia): This prescription medication is primarily for men and works by inhibiting the conversion of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone associated with male pattern baldness. It can slow down hair loss and, in some cases, promote regrowth.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: This treatment involves injecting a concentrated form of the patient’s own platelets into the scalp where hair is abundant to areas with thinning or balding.
Learn more in detail on PRP therapy for hair loss.
Hair Transplantation: Hair transplantation can be an option for some advanced cases of receding hairline. This surgical procedure involves relocating hair follicles from areas of the scalp where hair is abundant to areas with thinning or balding.
Lifestyle Changes: Managing stress, maintaining a healthy diet rich in essential nutrients, getting plenty of exercise and sleep, as well as avoiding harsh hair treatments can contribute to overall hair health.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Devices such as laser combs, helmets, or caps emit low-level laser light to the scalp, stimulating hair follicles and potentially promoting hair regrowth. LLLT may help slow down hair loss and improve hair density.
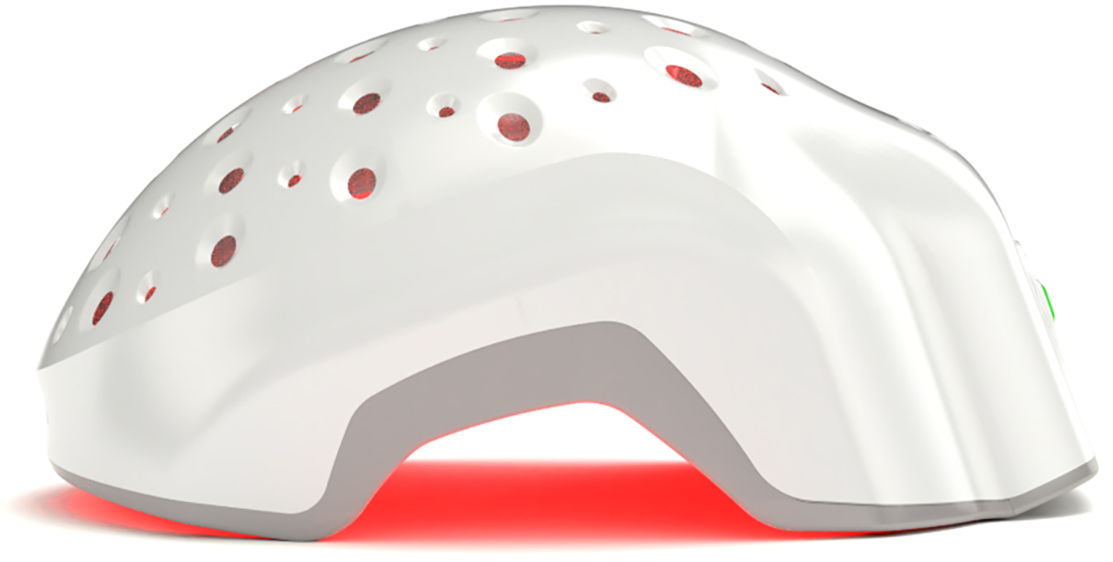
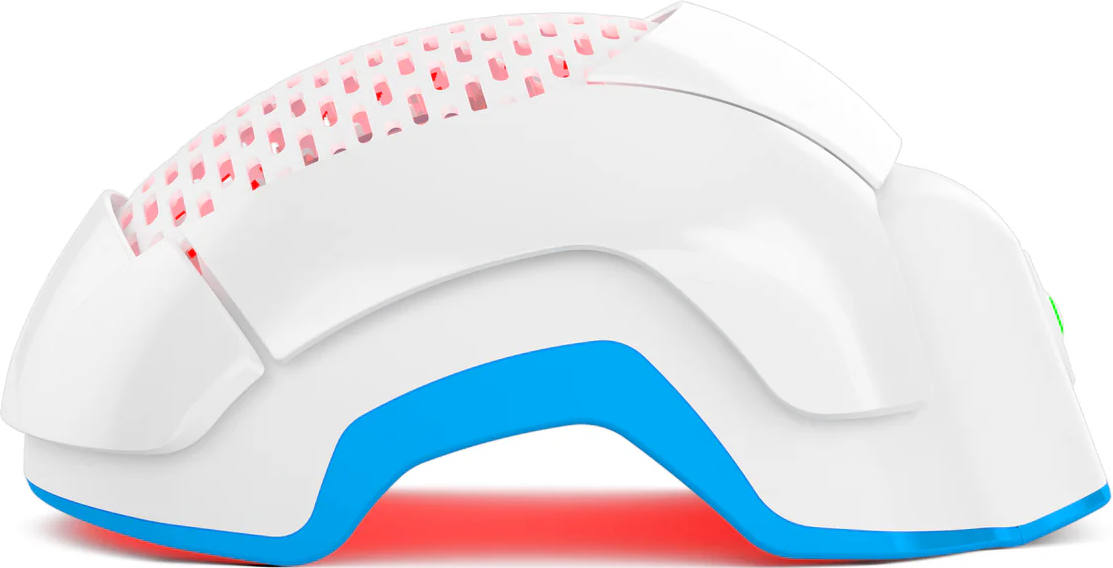
Theradome: A LLLT Device For Hair Loss
Theradome is a wearable, hands-free, low-level laser therapy device that promotes hair growth and reduces hair loss. It addresses issues like receding hairlines, thinning hair, and male or female pattern baldness.
Theradome emits red light at a specific wavelength (around 680 nanometers) directly on the scalp. The light energy is believed to stimulate cellular activity within the hair follicles. The light penetrates the scalp and gets absorbed by the cells, potentially increasing blood flow to the hair follicles. Improved circulation can provide essential nutrients to the hair follicles, promoting a healthier environment for hair growth.
Theradome is designed for ease of use, allowing individuals to undergo LLLT treatments conveniently at home without the need for clinic visits. Its hands-free design makes it relatively hassle-free during the treatment sessions.
Discover the potential of Theradome to stimulate your hair growth. Try Theradome today and take a step towards healthier, fuller hair. Explore the convenience of at-home LLLT treatments. Start your journey to stronger, thicker hair now!
Conclusion
Understanding a mature vs receding hairline is key to managing your hair health. A mature hairline is a normal part of aging and usually stabilizes over time, while a receding hairline often progresses and can lead to significant hair loss. Recognizing these differences early on allows you to choose appropriate treatments or lifestyle changes to maintain a healthy hairline. Remember, everyone's hair changes differently. If you're worried about your hairline, it's best to talk to a hair specialist. They can help you determine what's happening and suggest the right steps, whether embracing your new look or exploring treatment options.